NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE – WHY YOU SHOULD KNOW MORE ABOUT IT

Fatty liver is also known as hepatic steatosis. It happens when fat builds up in the liver. Having small amount of fat in your liver is normal. But when it is too much, you should really be worried about your health and even liver failure.
When fatty liver develops in someone who drinks a lot of alcohol, it is known as alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD). While the same in someone who doesn’t drink a lot of alcohol, this disease is known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
WHAT IS NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD)?
It is just as it sounds: fat in the liver but not due to too much alcohol consumption. Excess body weight and diabetes can increase your risk to get NAFLD. In fact according to a study published in EurekAlert, NAFLD in lean patients actually tends to be more deadly.

Fatty liver disease is when fat droplets deposit within the main cells (known as hepatocytes) in the liver, commonly due to excess fat, carbohydrates, and sugars in the diet.
Is fatty liver disease dangerous?
For many people fatty liver disease doesn’t cause liver damage, but in about a quarter of people, that fat will cause liver damage and possible liver scarring. Over time this inflammation and scarring can lead to the risk for liver cancer and impaired liver function.
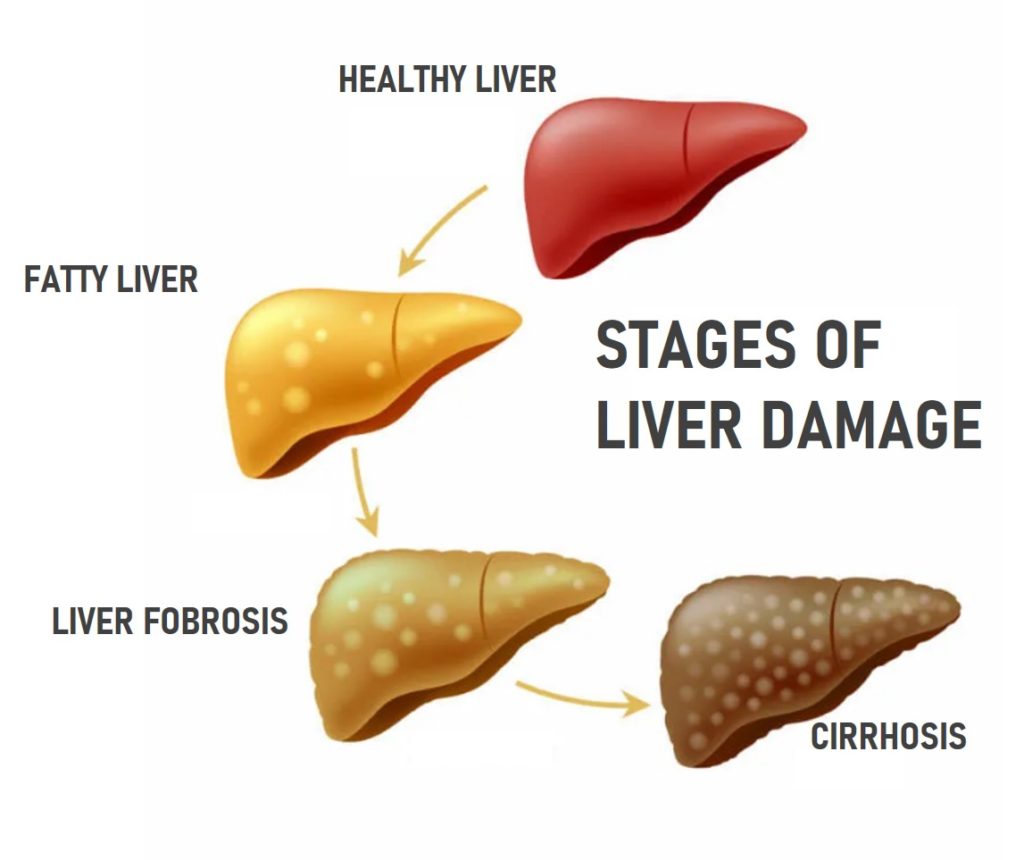
That’s why some people with cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver, or fibrosis) will need a liver transplant. Cirrhosis is a potentially life-threatening condition.
CAUSES OF NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
In people who don’t drink a lot of alcohol, the cause of fatty liver disease is less clear. But pre-diabetes, diabetes, and insulin resistance are all red flags. One or more of the following factors may play a role:
- Obesity
- High blood sugar
- Insulin resistance
- High levels of fat in your blood
- Exposure to certain toxins
- Certain genes may also raise your risk of developing fatty liver
SYMPTOMS OF NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
In many case non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is asymptomatic. But you may feel tired or experience discomfort or pain in the upper right side of your abdomen.
NAFLD may cause symptoms such as:
- loss of appetite
- weight loss
- fatigue
- weakness
- abdominal pain
- itchy skin
- swelling of your legs
- breast enlargement in men
WHAT TO DO IF YOU NON-ALCOHOLIC HAVE FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Although there are no medications approved to treat fatty liver disease. In many cases lifestyle changes can help reverse the fatty liver disease. For example, your doctor might advise you to:
- lose weight if needed
- exercise
- improve your diet
- limit or avoid alcohol
ENDING NOTE…
In many cases, it’s possible to reverse fatty liver through lifestyle changes. If you have serious condition, it increases your risk of liver cancer and liver failure. These complications can be fatal.
For the best outcome, it’s important to contact gastroenterologist and followre commended treatment plan and practice an overall healthy lifestyle.

